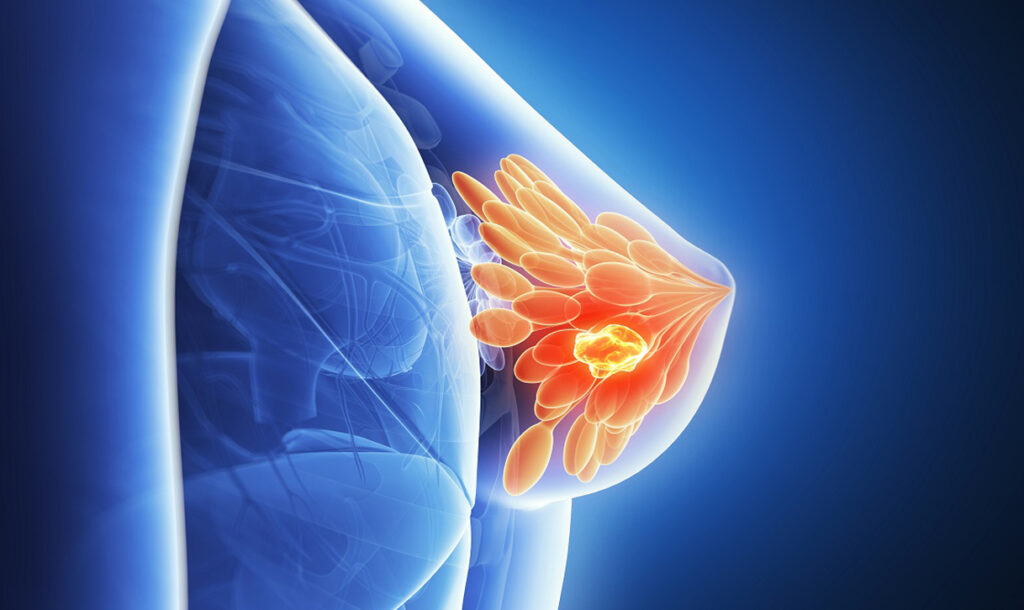
Breast cancer is the cancer that evolves in breast cells. Typically, the cancer builds in either the lobules or the ducts of the breast
Organic Fagonia cretica is used in different mixing combinations of Breast Cancer because for any patients with early diagnosis, leaf / flower / stem are of equal proportions in the herbal formulation, while for stage 4 / terminal cases, intake of Flower has to be increased uptil 90-95 %. We hereby request you to share illness details to us through email (AsmiConsultancyHerbals@gmail.com) or through clicking WhatsApp icon on this page below and we shall get back to you with our detailed analysis on the prescription / dosage. For each type / stage / origin of carcinoma, different mixing proportions with regards Organic Fagonia cretica (Leaf : Flower : Stem) are used so we can achieve maximum medicinal potency and the successful probability towards attaining a successful remission is higher.
Cancer happens when changes called mutations take place in genes that regulate cell growth and it’s the root cause. The mutations let the cells divide and multiply in an uncontrolled way resulting in the development of carcinoma which is fatal at times.
Breast cancer is the cancer that evolves in breast cells. Typically, the cancer builds in either the lobules or the ducts of the breast. Lobules are the glands that manufacture milk and ducts are the footpath that bring the milk from the glands to the nipple. Cancer can also happen in the tissue which is fatty or the fibrous connective tissue inside your breast.
The multiplied cancer cells often overrun other healthy breast tissue and can move to the lymph nodes under the arms. The lymph nodes are a primary way that help the cancer cells travel to other parts of the living body. See images and learn more about the formation of the breast.
Breast cancer symptoms
In its initial stages, breast cancer may not show any symptoms. In numerous cases, a tumor may be too small to be felt, but an abnormality can still be observed on a mammogram. If a tumor could be felt, the first sign is usually a fresh lump in the breast that was not there earlier. However, not all lumps can be called cancer.
Each type of breast cancer can show a variety of symptoms. Most of these symptoms are similar, but some could be different. Symptoms for the typical breast cancers include:
– a breast lump or tissue thickening that pretends different than surrounding tissue and has grown recently
– breast ache
– red, rough skin over your entire breast
– swelling in all or in some parts of your breast
– a nipple discharge rather than breast milk
– bloody discharge from your nipple
– peeling, scaling, or blister of skin on your nipple or breast
– an Uncertain, unexplained change in the shape or size of your breast
inverted nipple
– changes to the visible skin on your breasts
– a lump or swelling under your arm
If you face any of these symptoms, it doesn’t necessarily mean you are suffering from breast cancer. For an instance, ache in your breast or a breast lump can be caused by an amiable cyst. However, if you feel a lump in your breast or find other symptoms, you should see your doctor for further consultation, examination and testing. Learn more for possible symptoms of breast cancer.
Types of Breast Cancer
There are many types of breast cancer and they are divided into two major categories: “invasive” and “noninvasive,” or in situ. While invasive cancer has travelled from the breast ducts or glands to various parts of the breast, noninvasive cancer has not travelled from the natural tissue.
These four categories are used to explain the most common types of breast cancer, which consist:
– Ductal carcinoma inside situ. Ductal carcinoma inside situ (DCIS) is a noninvasive condition. With DCIS, the cancer cells are restricted to the ducts in your breast and haven’t invaded the surrounding tissue.
– Lobular carcinoma inside situ. Lobular carcinoma inside situ (LCIS) is cancer that grows in the milk-producing glands of the breast. Like DCIS, the cancer cells haven’t invaded the surrounding breast tissue.
– Invasive ductal carcinoma. Invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) is the most common variety of breast cancer. This variety of breast cancer starts in your breast’s milk ducts and then conquer nearby tissue in the breast. Once the breast cancer has travel to the tissue outside your milk ducts, it can start to spread to other surrounding organs and tissue.
– Invasive lobular carcinoma. Invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC) initially develops in your breast’s lobules and has invaded surrounding tissue.
Other, uncommon types of breast cancer consist:
– Paget disease of the nipple. This variety of breast cancer starts in the ducts of the nipple, but as it develops, it begins to impact the skin and areola of the nipple.
– Phyllodes tumor. This very uncommon type of breast cancer develops in the connective tissue of the breast. Most of these tumors are amiable, but some are cancerous.
– Angiosarcoma. This is cancer that grows on the blood vessels or lymph vessels inside the breast.
The type of cancer you have examines your treatment options, as well as your likely long-term result. Read more varieties of breast cancer.
Inflammatory breast cancer
Inflammatory breast cancer (IBC) is an uncommon but aggressive type of breast cancer. IBC counts up only between 1 to 5 percent Trusted Source of all breast cancer patients.
With this condition, cells choke the lymph nodes around the breasts, so the lymph vessels in the breast can’t properly outflow. Instead of developing a tumor, IBC does your breast to swell, look red and feel very warm. A cancerous breast may look like pitted and thick, like an orange peel.
IBC can be very aggressive and can grow quickly. For this type of aggressiveness, it’s important to call your doctor immediately if you find any symptoms. Find out more for IBC and the symptoms it can cause.
Triple-negative breast cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer is one other rare disease type, affecting only about 10 to 20 percent of patients with breast cancer. To be diagnosed as triple-negative breast cancer, a tumor necessarily have all three of the following characteristics:
– It lacks estrogen receptors. These are receptors on the cells that connect, or attach, to the hormone estrogen. If a tumor has estrogen receptors, estrogen can act as stimulator for the cancer to grow.
– It lacks progesterone receptors. These receptors are cells that attach to the hormone progesterone. If a tumor has progesterone receptors, progesterone can restore the cancer to grow.
– It doesn’t have additional HER2 proteins on its circumference. HER2 is a protein that increases breast cancer growth.
If a tumor meets these three parameter, it’s labeled a triple-negative breast cancer. This type of breast cancer has a capacity to grow and spread aggressively than other types of breast cancer.
Triple-negative breast cancers are tough to treat because hormonal therapy for breast cancer is very less effective. Learn more for treatments and survival rates about triple-negative breast cancer.
Metastatic breast cancer
Metastatic breast cancer is synonym for stage 4 breast cancer. It’s breast cancer that has grown from your breast to other body parts, such as your bones, lungs, or liver.
This is an later stage of breast cancer. Your oncologist (cancer doctor) will prepare a treatment plan with the intention of stopping the growth and spread of the tumor or tumors. Learn about treatment methods for metastatic cancer, also factors that impact your outlook.
Male breast cancer
Although in general they have less of it, men have breast tissue alike women do. Men can have breast cancer too, but it’s very rarer. According to the American Cancer Society (ACS), breast cancer is many more less 100 times to be precise less common in white men compared to white women, and many more less 70 times to be precise less common in black men than in black women.
It is said that, the breast cancer that men has is just as serious as the breast cancer women has. It has the same symptoms as well. Read more for breast cancer in men and the symptoms to take care for.
Breast cancer stages
Breast cancer could be divided into stages based on how big the tumor or tumors are and how much it has aggravated. Cancers that are large and/or have invaded surrounding tissues or organs are at a higher stage than cancers that are small and/or still inside the breast. In order to stage a breast cancer, doctors get to know:
– whether the cancer is invasive or noninvasive
– how vast the tumor is
– if the lymph nodes are involved
– if the cancer has grown to nearby tissue or organs
Breast cancer consist of five main stages: stages 0 to 5.
Stage 0 breast cancer
Stage 0 is DCIS. Cancer cells in DCIS stay confined to the ducts in the breast and have not grown into nearby tissue.
Stage 1 breast cancer
Stage 1A: The primary tumor is 2 centimeters wide or less and the lymph nodes are not impacted.
Stage 1B: Cancer is found in nearby lymph nodes, and either there has no tumor in the breast, or the tumor has smaller than 2 cm.
Stage 2 breast cancer
Stage 2A: The tumor has smaller than 2 cm and has travelled to 1–3 nearby lymph nodes, or it’s between 2 and 5 cm and hasn’t travelled to any lymph nodes.
Stage 2B: The tumor is between 2 and 5 cm and either has spread to 1–3 axillary (armpit) lymph nodes, or it’s larger than 5 cm and hasn’t travel to any lymph nodes.
Stage 3 breast cancer
Stage 3A:
The cancer has travelled to 4–9 axillary lymph nodes or has enlarged the internal mammary lymph nodes, and the primary tumor could be of different size.
Tumors are larger than 5 cm and the cancer has grown to 1–3 axillary lymph nodes or any of breastbone nodes.
Stage 3B: A tumor has invaded the chest wall or skin and may or may not have spread up to 9 lymph nodes.
Stage 3C: Cancer is found in 10 or more axillary lymph nodes, lymph nodes around the collarbone, or internal mammary nodes.
Stage 4 breast cancer
Stage 4 breast cancer can have a tumor of different size, and its cancer cells have grown to nearby and far lymph nodes as well as far organs.