Breast cancer is a malignant tumor that starts in the cells of the breast. A malignant tumor is a group of cancer cells that can grow into (invade) surrounding tissues or spread (metastasize) to distant areas of the body..
What is cancer?
The body is made up of trillions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide into new cells, and die in an orderly fashion. During the early years of a person’s life, normal cells divide faster to allow the person to grow. After the person becomes an adult, most cells divide only to replace worn-out or dying cells or to repair injuries.
Cancer begins when cells in a part of the body start to grow out of control. There are many kinds of cancer, but they all start because of out-of-control growth of abnormal cells. Cancer cell growth is different from normal cell growth. Instead of dying, cancer cells continue to grow and form new, abnormal cells. Cancer cells can also invade (grow into) other tissues, something that normal cells cannot do. Growing out of control and invading other tissues are what makes a cell a cancer cell.
Cells become cancer cells because of damage to DNA. DNA is in every cell and directs all its actions. In a normal cell, when DNA gets damaged the cell either repairs the damage or the cell dies. In cancer cells, the damaged DNA is not repaired, but the cell doesn’t die like it should. Instead, this cell goes on making new cells that the body does not need. These new cells will all have the same damaged DNA as the first cell does. People can inherit damaged DNA, but most DNA damage is caused by mistakes that happen while the normal cell is reproducing or by something in our environment. Sometimes the cause of the DNA damage is something obvious, like cigarette smoking. But often no clear cause is found. In most cases the cancer cells form a tumor. Some cancers, like leukemia, rarely form tumors. Instead, these cancer cells involve the blood and blood-forming organs and circulate through other tissues where they grow. Cancer cells often travel to other parts of the body, where they begin to grow and form new tumors that replace normal tissue. This process is called metastasis. It happens when the cancer cells get into the bloodstream or lymph vessels of our body. No matter where a cancer may spread, it is always named for the place where it started. For example, breast cancer that has spread to the liver is still called breast cancer, not liver cancer. Likewise, prostate cancer that has spread to the bone is metastatic prostate cancer, not bone cancer. Different types of cancer can behave very differently. For example, lung cancer and breast cancer are very different diseases. They grow at different rates and respond to different treatments. That is why people with cancer need treatment that is aimed at their particular kind of cancer. Not all tumors are cancerous. Tumors that aren’t cancer are called benign. Benign tumors can cause problems – they can grow very large and press on healthy organs and tissues. But they cannot grow into (invade) other tissues. Because they can’t invade, they also can’t spread to other parts of the body (metastasize). These tumors are almost never life threatening.
What is breast cancer?
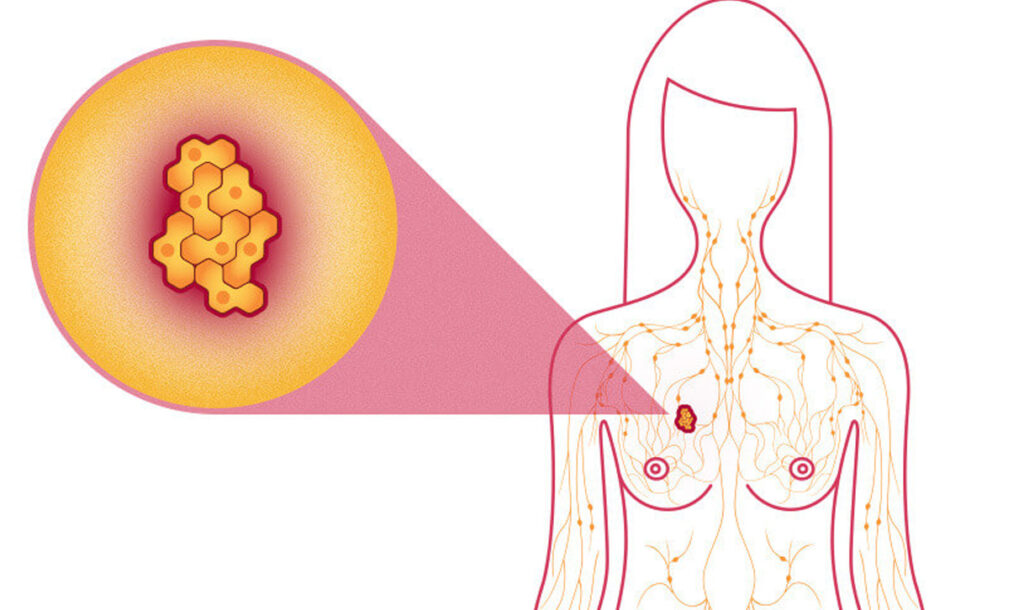
Breast cancer is a malignant tumor that starts in the cells of the breast. A malignant tumor is a group of cancer cells that can grow into (invade) surrounding tissues or spread (metastasize) to distant areas of the body. The disease occurs almost entirely in women, but men can get it, too. The remainder of this document refers only to breast cancer in women. For information on breast cancer in men, see our document, Breast Cancer in Men.
The normal breast
To understand breast cancer, it helps to have some basic knowledge about the normal structure of the breasts, shown in the diagram below. The female breast is made up mainly of lobules (milk-producing glands), ducts (tiny tubes that carry the milk from the lobules to the nipple), and stroma (fatty tissue and connective tissue surrounding the ducts and lobules, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels). Most breast cancers begin in the cells that line the ducts (ductal cancers). Some begin in the cells that line the lobules (lobular cancers), while a small number start in other tissues.
The lymph (lymphatic) system of the breast
The lymph system is important to understand because it is one way breast cancers can spread. This system has several parts. Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped collections of immune system cells (cells that are important in fighting infections) that are connected by lymphatic vessels. Lymphatic vessels are like small veins, except that they carry a clear fluid called lymph (instead of blood) away from the breast. Lymph contains tissue fluid and waste products, as well as immune system cells. Breast cancer cells can enter lymphatic vessels and begin to grow in lymph nodes. Most lymphatic vessels in the breast connect to lymph nodes under the arm (axillary nodes). Some lymphatic vessels connect to lymph nodes inside the chest (internal mammary nodes) and those either above or below the collarbone (supraclavicular or infraclavicular nodes). If the cancer cells have spread to lymph nodes, there is a higher chance that the cells could have also gotten into the bloodstream and spread (metastasized) to other sites in the body. The more lymph nodes that have breast cancer, the more likely it is that the cancer may be found in other organs as well. Because of this, finding cancer in one or more lymph nodes often affects the treatment plan. Still, not all women with cancer cells in
their lymph nodes develop metastases, and some women can have no cancer cells in their lymph nodes and later develop metastases.
Benign breast lumps
Most breast lumps are not cancerous (benign). Still, some may need to be sampled and viewed under a microscope to prove they are not cancer.
Fibrosis and cysts
Most lumps turn out to be caused by fibrosis and/or cysts, benign changes in the breast tissue that happen in many women at some time in their lives. (This is sometimes called fibrocystic changes and used to be called fibrocystic disease.) Fibrosis is the formation of scar-like (fibrous) tissue, and cysts are fluid-filled sacs. These conditions are most often diagnosed by a doctor based on symptoms, such as breast lumps, swelling, and tenderness or pain. These symptoms tend to be worse just before a woman’s menstrual period is about to begin. Her breasts may feel lumpy and, sometimes, she may notice a clear or slightly cloudy nipple discharge.
Fibroadenomas and intraductal papillomas
Benign breast tumors such as fibroadenomas or intraductal papillomas are abnormal growths, but they are not cancerous and do not spread outside the breast to other organs. They are not life threatening. Still, some benign breast conditions are important because women with these conditions have a higher risk of developing breast cancer. For more information see the section, “What are the risk factors for breast cancer?” and our document, Non-cancerous Breast Conditions.
General breast cancer terms
Here are some of the key words used to describe breast cancer.
Carcinoma
This is a term used to describe a cancer that begins in the lining layer (epithelial cells) of organs like the breast. Nearly all breast cancers are carcinomas (either ductal carcinomas or lobular carcinomas).
Adenocarcinoma
An adenocarcinoma is a type of carcinoma that starts in glandular tissue (tissue that makes and secretes a substance). The ducts and lobules of the breast are glandular tissues (they make breast milk), so cancers starting in these areas are often called adenocarcinomas.
Carcinoma in situ
This term is used for an early stage of cancer, when it is confined to the layer of cells where it began. In breast cancer, in situ means that the cancer cells remain confined to ducts (ductal carcinoma in situ). The cells have not grown into (invaded) deeper tissues in the breast or spread to other organs in the body. Carcinoma in situ of the breast is sometimes referred to as non-invasive or pre-invasive breast cancer because it might develop into an invasive breast cancer if left untreated. When cancer cells are confined to the lobules it is called lobular carcinoma in situ. This is not actually a true cancer or pre-cancer, and is discussed more in the section, “What are the risk factors for breast cancer?â€
Invasive (infiltrating) carcinoma
An invasive cancer is one that has already grown beyond the layer of cells where it started (as opposed to carcinoma in situ). Most breast cancers are invasive carcinomas— either invasive ductal carcinoma or invasive lobular carcinoma.
Sarcoma
Sarcomas are cancers that start in connective tissues such as muscle tissue, fat tissue, or blood vessels. Sarcomas of the breast are rare.
Types of breast cancers
There are several types of breast cancer, but some of them are quite rare. In some cases a single breast tumor can be a combination of these types or be a mixture of invasive and in situ cancer.
Ductal carcinoma in situ
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS; also known as intraductal carcinoma) is the most common type of non-invasive breast cancer. DCIS means that the cancer cells are inside the ducts but have not spread through the walls of the ducts into the surrounding breast tissue. About 1 in 5 new breast cancer cases will be DCIS. Nearly all women diagnosed at this early stage of breast cancer can be cured. A mammogram is often the best way to find DCIS early.
When DCIS is diagnosed, the pathologist (a doctor specializing in diagnosing disease from tissue samples) will look for areas of dead or dying cancer cells, called tumor necrosis, within the tissue sample. If necrosis is present, the tumor is likely to be more aggressive. The term comedocarcinoma is often used to describe DCIS with large areas of necrosis. The pathologist will also note how abnormal the cells appear, especially the part of cells where DNA is found (the nucleus).
Lobular carcinoma in situ
This is not a true cancer or pre-cancer, and is discussed in the section “What are the risk factors for breast cancer?†Invasive (or infiltrating) ductal carcinoma This is the most common type of breast cancer. Invasive (or infiltrating) ductal carcinoma (IDC) starts in a milk duct of the breast, breaks through the wall of the duct, and grows into the fatty tissue of the breast. At this point, it may be able to spread (metastasize) to other parts of the body through the lymphatic system and bloodstream. About 8 of 10 invasive breast cancers are infiltrating ductal carcinomas.
Invasive (or infiltrating) lobular carcinoma
Invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC) starts in the milk-producing glands (lobules). Like IDC, it can spread (metastasize) to other parts of the body. About 1 invasive breast cancer in 10 is an ILC. Invasive lobular carcinoma may be harder to detect by a mammogram than invasive ductal carcinoma.
Less common types of breast cancer
Inflammatory breast cancer: This uncommon type of invasive breast cancer accounts for about 1% to 3% of all breast cancers. Usually there is no single lump or tumor. Instead, inflammatory breast cancer (IBC) makes the skin on the breast look red and feel warm. It also may give the breast skin a thick, pitted appearance that looks a lot like an orange peel. Doctors now know that these changes are not caused by inflammation or infection, but by cancer cells blocking lymph vessels in the skin. The affected breast may become larger or firmer, tender, or itchy. In its early stages, inflammatory breast cancer is often mistaken for an infection in the breast (called mastitis) and treated as an infection with antibiotics. If the symptoms are caused by cancer, they will not improve, and a biopsy will find cancer cells. Because there is no actual lump, it might not show up on a mammogram, which can make it even harder to find it early. This type of breast cancer tends to have a higher chance of spreading and a worse outlook (prognosis) than typical invasive ductal or lobular cancer. For more details about this condition, see our document, Inflammatory Breast Cancer.
Triple-negative breast cancer:
This term is used to describe breast cancers (usually invasive ductal carcinomas) whose cells lack estrogen receptors and progesterone receptors, and do not have an excess of the HER2 protein on their surfaces. (See the section, “How is breast cancer diagnosed?” for more detail on these receptors.) Breast cancers with these characteristics tend to occur more often in younger women and in African-American women. Triple-negative breast cancers tend to grow and spread more quickly than most other types of breast cancer. Because the tumor cells lack these certain receptors, neither hormone therapy nor drugs that target HER2 are effective treatments (but chemotherapy can still be useful if needed).
Paget disease of the nipple:
This type of breast cancer starts in the breast ducts and spreads to the skin of the nipple and then to the areola, the dark circle around the nipple. It is rare, accounting for only about 1% of all cases of breast cancer. The skin of the nipple and areola often appears crusted, scaly, and red, with areas of bleeding or oozing. The woman may notice burning or itching. Paget disease is almost always associated with either ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) or infiltrating ductal carcinoma. Treatment often requires mastectomy. If no lump can be felt in the breast tissue, and the biopsy shows DCIS but no invasive cancer, the outlook (prognosis) is excellent. If invasive cancer is present, the prognosis is not as good, and the cancer will need to be staged and treated like any other invasive cancer.
Phyllodes tumor:
This very rare breast tumor develops in the stroma (connective tissue) of the breast, in contrast to carcinomas, which develop in the ducts or lobules. Other names for these tumors include phylloides tumor and cystosarcoma phyllodes. These tumors are usually benign but on rare occasions may be malignant. Benign phyllodes tumors are treated by removing the tumor along with a margin of normal breast tissue. A malignant phyllodes tumor is treated by removing it along with a wider margin of normal tissue, or by mastectomy. Surgery is often all that is needed, but these cancers might not respond as well to the other treatments used for more common breast cancers. When a malignant phyllodes tumor has spread, it can be treated with the chemotherapy given for soft-tissue sarcomas (this is discussed in detail in our document, Sarcoma – Adult Soft Tissue Cancer.
Angiosarcoma: This form of cancer starts in cells that line blood vessels or lymph vessels. It rarely occurs in the breasts. When it does, it usually develops as a complication of previous radiation treatments. This is an extremely rare complication of breast radiation therapy that can develop about 5 to 10 years after radiation. Angiosarcoma can also occur in the arms of women who develop lymphedema as a result of lymph node surgery or radiation therapy to treat breast cancer. (For information on lymphedema, see the section, “How is breast cancer treated?”) These cancers tend to grow and spread quickly. Treatment is generally the same as for other sarcomas. See our document, Sarcoma – Adult Soft Tissue Cancer.
Special types of invasive breast carcinoma
There are some special types of breast cancer that are sub-types of invasive carcinoma. These are often named after features seen when they are viewed under the microscope, like the ways the cells are arranged. Some of these may have a better prognosis than standard infiltrating ductal carcinoma.
These include:
• Adenoid cystic (or adenocystic) carcinoma
• Low-grade adenosquamous carcinoma (this is a type of metaplastic carcinoma) • Medullary carcinoma
• Mucinous (or colloid) carcinoma
• Papillary carcinoma
• Tubular carcinoma
Some sub-types have the same or maybe worse prognosis than standard infiltrating ductal carcinoma. These include:
• Metaplastic carcinoma (most types, including spindle cell and squamous)
• Micropapillary carcinoma
• Mixed carcinoma (has features of both invasive ductal and lobular)
In general, all of these sub-types are still treated like standard infiltrating ductal carcinoma.
What are the key statistics about breast cancer?
Breast cancer is the most common cancer among American women, except for skin cancers. About 1 in 8 (12%) women in the US will develop invasive breast cancer during their lifetime.
The American Cancer Society’s estimates for breast cancer in the United States are for 2013:
• About 232,340 new cases of invasive breast cancer will be diagnosed in women.
• About 64,640 new cases of carcinoma in situ (CIS) will be diagnosed (CIS is noninvasive and is the earliest form of breast cancer).
• About 39,620 women will die from breast cancer
After increasing for more than 2 decades, female breast cancer incidence rates began decreasing in 2000, then dropped by about 7% from 2002 to 2003. This large decrease was thought to be due to the decline in use of hormone therapy after menopause that occurred after the results of the Women’s Health Initiative were published in 2002. This study linked the use of hormone therapy to an increased risk of breast cancer and heart diseases. Incidence rates have been stable in recent years.
Breast cancer is the second leading cause of cancer death in women, exceeded only by lung cancer. The chance that breast cancer will be responsible for a woman’s death is about 1 in 36 (about 3%). Death rates from breast cancer have been declining since about1989, with larger decreases in women younger than 50. These decreases are believed to be the result of earlier detection through screening and increased awareness, as well as improved treatment.
At this time there are more than 2.9 million breast cancer survivors in the United States. (This includes women still being treated and those who have completed treatment.) Survival rates are discussed in the section “How is breast cancer staged?â€
What are the risk factors for breast cancer?
A risk factor is anything that affects your chance of getting a disease, such as cancer. Different cancers have different risk factors. For example, exposing skin to strong sunlight is a risk factor for skin cancer. Smoking is a risk factor for cancers of the lung, mouth, larynx (voice box), bladder, kidney, and several other organs. But risk factors don’t tell us everything. Having a risk factor, or even several, does not mean that you will get the disease. Most women who have one or more breast cancer risk factors never develop the disease, while many women with breast cancer have no
apparent risk factors (other than being a woman and growing older). Even when a woman with risk factors develops breast cancer, it is hard to know just how much these factors might have contributed.
There are different kinds of risk factors. Some factors, like a person’s age or race, can’t be changed. Others are linked to cancer-causing factors in the environment. Still others are related personal behaviors, such as smoking, drinking, and diet. Some factors influence risk more than others, and your risk for breast cancer can change over time, due to factors such as aging or lifestyle.
Risk factors you cannot change
Gender
Simply being a woman is the main risk factor for developing breast cancer. Men can develop breast cancer, but this disease is about 100 times more common among women than men. This is likely because men have less of the female hormones estrogen and progesterone, which can promote breast cancer cell growth
Aging
Your risk of developing breast cancer increases as you get older. About 1 out of 8 invasive breast cancers are found in women younger than 45, while about 2 of 3 invasive breast cancers are found in women age 55 or older.
Genetic risk factors
About 5% to 10% of breast cancer cases are thought to be hereditary, resulting directly from gene defects (called mutations) inherited from a parent. See the section, “Do we know what causes breast cancer?” for more information about genes and DNA.
BRCA1 and BRCA2: The most common cause of hereditary breast cancer is an inherited mutation in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes. In normal cells, these genes help prevent cancer by making proteins that keep the cells from growing abnormally. If you have inherited a mutated copy of either gene from a parent, you have a high risk of developing breast cancer during your lifetime. The risk may be as high as 80% for members of some families with BRCA mutations. These cancers tend to occur in younger women and more often affect both breasts than cancers in women who are not born with one of these gene mutations. Women with these inherited mutations also have an increased risk for developing other cancers, particularly ovarian cancer.
In the United States BRCA mutations are more common in Jewish women of Ashkenazi (Eastern Europe) origin than in other racial and ethnic groups, but they can occur in any racial or ethnic group.
Changes in other genes: Other gene mutations can also lead to inherited breast cancers. These gene mutations are much rarer and often do not increase the risk of breast cancer as much as the BRCA genes. They are not frequent causes of inherited breast cancer.
• ATM: The ATM gene normally helps repair damaged DNA. Inheriting 2 abnormal copies of this gene causes the disease ataxia-telangiectasia. Inheriting 1 mutated copy of this gene has been linked to a high rate of breast cancer in some families.
• TP53: The TP53 gene gives instructions for making a protein called p53 that helps stop the growth of abnormal cells. Inherited mutations of this gene cause Li-Fraumeni syndrome (named after the 2 researchers who first described it). People with this syndrome have an increased risk of developing breast cancer, as well as several other cancers such as leukemia, brain tumors, and sarcomas (cancer of bones or connective tissue). This is a rare cause of breast cancer.
• CHEK2: The Li-Fraumeni syndrome can also be caused by inherited mutations in the CHEK2 gene. Even when it does not cause this syndrome, it can increase breast cancer risk about twofold when it is mutated.
• PTEN: The PTEN gene normally helps regulate cell growth. Inherited mutations in this gene can cause Cowden syndrome, a rare disorder in which people are at increased risk for both benign and malignant breast tumors, as well as growths in the digestive tract, thyroid, uterus, and ovaries. Defects in this gene can also cause a different syndrome called Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome that is not thought to be linked to breast cancer risk.
• CDH1: Inherited mutations in this gene cause hereditary diffuse gastric cancer, a syndrome in which people develop a rare type of stomach cancer at an early age. Women with mutations in this gene also have an increased risk of invasive lobular breast cancer.
• STK11: Defects in this gene can lead to Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. People with this disorder develop pigmented spots on their lips and in their mouths, polyps in the urinary and gastrointestinal tracts, and have an increased risk of many types of cancer, including breast cancer. Genetic testing: Genetic tests can be done to look for mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes (or some other genes linked to breast cancer risk). Although testing may be helpful in some situations, the pros and cons need to be considered carefully. For more information, see the section, “Can breast cancer be prevented?”
Family history of breast cancer
Breast cancer risk is higher among women whose close blood relatives have this disease. Having one first-degree relative (mother, sister, or daughter) with breast cancer approximately doubles a woman’s risk. Having 2 first-degree relatives increases her risk about 3-fold. The exact risk is not known, but women with a family history of breast cancer in a father or brother also have an increased risk of breast cancer. Altogether, less than 15% of women with breast cancer have a family member with this disease. This means that most (over 85%) women who get breast cancer do not have a family history of this disease.
Personal history of breast cancer
A woman with cancer in one breast has a 3- to 4-fold increased risk of developing a new cancer in the other breast or in another part of the same breast. This is different from a recurrence (return) of the first cancer.
Race and ethnicity
Overall, white women are slightly more likely to develop breast cancer than are AfricanAmerican women, but African-American women are more likely to die of this cancer. However, in women under 45 years of age, breast cancer is more common in African- American women. Asian, Hispanic, and Native-American women have a lower risk of developing and dying from breast cancer.
Dense breast tissue
Breasts are made up of fatty tissue, fibrous tissue, and glandular tissue. Someone is said to have dense breast tissue (as seen on a mammogram) when they have more glandular and fibrous tissue and less fatty tissue. Women with dense breasts have a higher risk of breast cancer than women with less dense breasts. Unfortunately, dense breast tissue can also make mammograms less accurate.
A number of factors can affect breast density, such as age, menopausal status, the use of drugs (such as menopausal hormone therapy), pregnancy, and genetics.
Certain benign breast conditions
Women diagnosed with certain benign breast conditions might have an increased risk of breast cancer. Some of these conditions are more closely linked to breast cancer risk than others. Doctors often divide benign breast conditions into 3 general groups, depending on how they affect this risk.
Non-proliferative lesions: These conditions are not associated with overgrowth of breast tissue. They do not seem to affect breast cancer risk, or if they do, it is to a very small extent. They include:
• Fibrosis and/or simple cysts (this used to be called fibrocystic disease or changes)
• Mild hyperplasia
• Adenosis (non-sclerosing)
• Ductal ectasia
• Phyllodes tumor (benign)
• A single papilloma
• Fat necrosis
• Periductal fibrosis
• Squamous and apocrine metaplasia
• Epithelial-related calcifications
• Mastitis (infection of the breast)
• Other benign tumors (lipoma, hamartoma, hemangioma, neurofibroma, adenomyoepthelioma) Proliferative lesions without atypia: These conditions show excessive growth of cells in the ducts or lobules of the breast tissue. They seem to raise a woman’s risk of breast cancer slightly (1½ to 2 times normal).
They include:
• Usual ductal hyperplasia (without atypia)
• Fibroadenoma
• Sclerosing adenosis
• Several papillomas (called papillomatosis)
• Radial scar
Proliferative lesions with atypia: In these conditions, there is an overgrowth of cells in the ducts or lobules of the breast tissue, with some of the cells no longer appearing normal. They have a stronger effect on breast cancer risk, raising it 3 1/2 to 5 times higher than normal. These types of lesions include:
• Atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH)
• Atypical lobular hyperplasia (ALH)
Women with a family history of breast cancer and either hyperplasia or atypical hyperplasia have an even higher risk of developing a breast cancer.
For more information on these conditions, see our document, Non-cancerous Breast Conditions.
Lobular carcinoma in situ
In lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) cells that look like cancer cells are growing in the lobules of the milk-producing glands of the breast, but they do not grow through the wall of the lobules. LCIS (also called lobular neoplasia) is sometimes grouped with ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) as a non-invasive breast cancer, but it differs from DCIS in that it doesn’t seem to become an invasive cancer if it isn’t treated. Women with this condition have a 7- to 11-fold increased risk of developing invasive cancer in either breast. For this reason, women with LCIS should make sure they have regular mammograms and doctor visits.
Menstrual periods
Women who have had more menstrual cycles because they started menstruating early (before age 12) and/or went through menopause later (after age 55) have a slightly higher risk of breast cancer. The increase in risk may be due to a longer lifetime exposure to the hormones estrogen and progesterone. Previous chest radiation Women who, as children or young adults, had radiation therapy to the chest area as treatment for another cancer (such as Hodgkin disease or non-Hodgkin lymphoma) have a significantly increased risk for breast cancer. This varies with the patient’s age when they had radiation. If chemotherapy was also given, it may have stopped ovarian hormone production for some time, lowering the risk. The risk of developing breast cancer from chest radiation is highest if the radiation was given during adolescence, when the breasts were still developing. Radiation treatment after age 40 does not seem to increase breast cancer risk.
Diethylstilbestrol exposure
From the 1940s through the 1960s some pregnant women were given the drug diethylstilbestrol (DES) because it was thought to lower their chances of miscarriage (losing the baby). These women have a slightly increased risk of developing breast cancer. Women whose mothers took DES during pregnancy may also have a slightly higher risk of breast cancer.
Exposure: Questions and Answers.
Lifestyle-related factors and breast cancer risk
Having children
Women who have had no children or who had their first child after age 30 have a slightly higher breast cancer risk. Having many pregnancies and becoming pregnant at a young age reduce breast cancer risk. Pregnancy reduces a woman’s total number of lifetime menstrual cycles, which may be the reason for this effect.
Birth control
Recent oral contraceptive use: Studies have found that women using oral contraceptives (birth control pills) have a slightly greater risk of breast cancer than women who have never used them. This risk seems to go back to normal over time once the pills are stopped. Women who stopped using oral contraceptives more than 10 years ago do not appear to have any increased breast cancer risk. When thinking about using oral contraceptives, women should discuss their other risk factors for breast cancer with their health care team.
Depot-medroxyprogesterone acetate (DMPA; Depo-Provera® ) is an injectable form of progesterone that is given once every 3 months as birth control. A few studies have looked at the effect of DMPA on breast cancer risk. Women currently using DMPA seem to have an increase in risk, but the risk doesn’t seem to be increased if this drug was used more than 5 years ago.
Hormone therapy after menopause
Hormone therapy with estrogen (often combined with progesterone) has been used for many years to help relieve symptoms of menopause and to help prevent osteoporosis (thinning of the bones). Earlier studies suggested it might have other health benefits as well, but these benefits have not been found in more recent, better designed studies. This treatment goes by many names, such as post-menopausal hormone therapy (PHT), hormone replacement therapy (HRT), and menopausal hormone therapy (MHT).
There are 2 main types of hormone therapy. For women who still have a uterus (womb), doctors generally prescribe both estrogen and progesterone (known as combined hormone therapy or HT). Progesterone is needed because estrogen alone can increase the risk of cancer of the uterus. For women who no longer have a uterus (those who’ve had a hysterectomy), estrogen alone can be prescribed. This is commonly known as estrogen replacement therapy (ERT) or just estrogen therapy (ET).
Combined hormone therapy: Using combined hormone therapy after menopause increases the risk of getting breast cancer. It may also increase the chances of dying from breast cancer. This increase in risk can be seen with as little as 2 years of use. Combined HT also increases the likelihood that the cancer may be found at a more advanced stage. The increased risk from combined hormone therapy appears to apply only to current and recent users. A woman’s breast cancer risk seems to return to that of the general population within 5 years of stopping combined treatment. The word bioidentical is sometimes used to describe versions of estrogen and progesterone with the same chemical structure as those found naturally in people. The use of these hormones has been marketed as a safe way to treat the symptoms of menopause. It is important to realize that although there are few studies comparing “bioidentical” or “natural†hormones to synthetic versions of hormones, there is no evidence that they are safer or more effective. The use of these bioidentical hormones should be assumed to have the same health risks as any other type of hormone therapy.
Estrogen therapy (ET): The use of estrogen alone after menopause does not appear to increase the risk of developing breast cancer. In fact, some research has suggested that women who have previously had their uterus removed and who take estrogen actually have a lower risk of breast cancer. Women taking estrogen seem to have more problems with strokes and other blood clots, though. Also, when used long term (for more than 10 years), ET has been found to increase the risk of ovarian cancer in some studies. At this time there appear to be few strong reasons to use post-menopausal hormone therapy (either combined HT or ET), other than possibly for the short-term relief of menopausal symptoms. Along with the increased risk of breast cancer, combined HT also appears to increase the risk of heart disease, blood clots, and strokes. It does lower the risk of colorectal cancer and osteoporosis, but this must be weighed against possible harm, especially since there are other effective ways to prevent and treat osteoporosis. Although ET does not seem to increase breast cancer risk, it does increase the risk of blood clots and stroke.
The decision to use hormone therapy after menopause should be made by a woman and her doctor after weighing the possible risks and benefits, based on the severity of her menopausal symptoms and the woman’s other risk factors for heart disease, breast cancer, and osteoporosis. If a woman and her doctor decide to try hormones for symptoms of menopause, it is usually best to use it at the lowest dose needed to control symptoms and for as short a time as possible.
Breastfeeding
Some studies suggest that breastfeeding may slightly lower breast cancer risk, especially if breastfeeding is continued for 1½ to 2 years. But this has been a difficult area to study, especially in countries such as the United States, where breastfeeding for this long is uncommon. One explanation for this possible effect may be that breastfeeding reduces a woman’s total number of lifetime menstrual cycles (similar to starting menstrual periods at a later age or going through early menopause).
Alcohol
The use of alcohol is clearly linked to an increased risk of developing breast cancer. The risk increases with the amount of alcohol consumed. Compared with non-drinkers, women who consume 1 alcoholic drink a day have a very small increase in risk. Those who have 2 to 5 drinks daily have about 1½ times the risk of women who don’t drink alcohol. Excessive alcohol use is also known to increase the risk of developing several other types of cancer.
Being overweight or obese
Being overweight or obese after menopause increases breast cancer risk. Before menopause your ovaries produce most of your estrogen, and fat tissue produces a small amount of estrogen. After menopause (when the ovaries stop making estrogen), most of a woman’s estrogen comes from fat tissue. Having more fat tissue after menopause can increase your chance of getting breast cancer by raising estrogen levels. Also, women
who are overweight tend to have higher blood insulin levels. Higher insulin levels have also been linked to some cancers, including breast cancer. But the connection between weight and breast cancer risk is complex. For example, the risk appears to be increased for women who gained weight as an adult but may not be increased among those who have been overweight since childhood. Also, excess fat in the waist area may affect risk more than the same amount of fat in the hips and thighs. Researchers believe that fat cells in various parts of the body have subtle differences that may explain this.
Physical activity
Evidence is growing that physical activity in the form of exercise reduces breast cancer risk. The main question is how much exercise is needed. In one study from the Women’s Health Initiative, as little as 1.25 to 2.5 hours per week of brisk walking reduced a woman’s risk by 18%. Walking 10 hours a week reduced the risk a little more. Factors with uncertain, controversial, or unproven effect on breast cancer risk
Diet and vitamin intake
Many studies have looked for a link between what women eat and breast cancer risk, but so far the results have been conflicting. Some studies have indicated that diet may play a role, while others found no evidence that diet influences breast cancer risk. Studies have looked at the amount of fat in the diet, intake of fruits and vegetables, and intake of meat. No clear link to breast cancer risk was found. Studies have also looked at vitamin levels, again with inconsistent results. Some studies actually found an increased risk of breast cancer in women with higher levels of certain nutrients. So far, no study has shown that taking vitamins reduces breast cancer risk. This is not to say that there is no point in eating a healthy diet. A diet low in fat, low in red meat and processed meat, and high in fruits and vegetables might have other health benefits.
Most studies have found that breast cancer is less common in countries where the typical diet is low in total fat, low in polyunsaturated fat, and low in saturated fat. But many studies of women in the United States have not linked breast cancer risk to dietary fat intake. Researchers are still not sure how to explain this apparent disagreement. It may be at least partly due to the effect of diet on body weight (see below). Also, studies comparing diet and breast cancer risk in different countries are complicated by other differences (like activity level, intake of other nutrients, and genetic factors) that might also affect breast cancer risk.
More research is needed to understand the effect of the types of fat eaten on breast cancer risk. But it is clear that calories do count, and fat is a major source of calories. High-fat diets can lead to being overweight or obese, which is a breast cancer risk factor. A diet high in fat has also been shown to influence the risk of developing several other types of cancer, and intake of certain types of fat is clearly related to heart disease risk.
Antiperspirants
Internet e-mail rumors have suggested that chemicals in underarm antiperspirants are absorbed through the skin, interfere with lymph circulation, cause toxins to build up in the breast, and eventually lead to breast cancer. There is very little evidence to support this rumor. One small study found trace levels of parabens (used as preservatives in antiperspirants and other products), which have weak estrogen-like properties, in a small sample of breast cancer tumors. But this study did not look at whether parabens caused the tumors. This was a preliminary finding, and more research is needed to determine what effect, if any, parabens may have on breast cancer risk. On the other hand, a large study of breast cancer causes found no increase in breast cancer in women who used underarm antiperspirants and/or shaved their underarms.
Bras
Internet e-mail rumors and at least one book have suggested that bras cause breast cancer by obstructing lymph flow. There is no good scientific or clinical basis for this claim. Women who do not wear bras regularly are more likely to be thinner or have less dense breasts, which would probably contribute to any perceived difference in risk.
Induced abortion
Several studies have provided very strong data that neither induced abortions nor spontaneous abortions (miscarriages) have an overall effect on the risk of breast cancer.
Breast implants
Several studies have found that breast implants do not increase the risk of breast cancer, although silicone breast implants can cause scar tissue to form in the breast. Implants make it harder to see breast tissue on standard mammograms, but additional x-ray pictures called implant displacement views can be used to examine the breast tissue more completely. Breast implants may be linked to a rare type of lymphoma called anaplastic large cell lymphoma. This lymphoma has rarely been found in the breast tissue around the implants. So far, though, there are too few cases to know if the risk of this lymphoma is really higher in women that have implants.
Chemicals in the environment
A great deal of research has been reported and more is being done to understand possible environmental influences on breast cancer risk.
Compounds in the environment that studies in lab animals have found to have estrogenlike properties are of special interest. These could in theory affect breast cancer risk. For example, substances found in some plastics, certain cosmetics and personal care products, pesticides (such as DDE), and PCBs (polychlorinated biphenyls) seem to have such properties. This issue understandably invokes a great deal of public concern, but at this time research does not show a clear link between breast cancer risk and exposure to these substances. Unfortunately, studying such effects in humans is difficult. More research is needed to better define the possible health effects of these and similar substances.
Tobacco smoke
For a long time, studies found no link between cigarette smoking and breast cancer. In recent years though, more studies have found that long-term heavy smoking is linked to a higher risk of breast cancer. Some studies have found that the risk is highest in certain groups, such as women who started smoking when they were young. In 2009, the International Agency for Research on Cancer concluded that there is limited evidence that tobacco smoking causes breast cancer. An active focus of research is whether secondhand smoke increases the risk of breast cancer. Both mainstream and secondhand smoke contain chemicals that, in high concentrations, cause breast cancer in rodents. Chemicals in tobacco smoke reach breast tissue and are found in breast milk.
The evidence on secondhand smoke and breast cancer risk in human studies is controversial, at least in part because the link between smoking and breast cancer hasn’t been clear. One possible explanation for this is that tobacco smoke may have different effects on breast cancer risk in smokers and in those who are just exposed to smoke. A report from the California Environmental Protection Agency in 2005 concluded that the evidence about secondhand smoke and breast cancer is “consistent with a causal association” in younger, mainly premenopausal women. The 2006 US Surgeon General’s report, The Health Consequences of Involuntary Exposure to Tobacco Smoke, concluded that there is “suggestive but not sufficient” evidence of a link at this point. In any case, this possible link to breast cancer is yet another reason to avoid secondhand smoke. Night work Several studies have suggested that women who work at night—for example, nurses on a night shift—may have an increased risk of developing breast cancer. This is a fairly recent finding, and more studies are looking at this issue. Some researchers think the effect may be due to changes in levels of melatonin, a hormone whose production is affected by the body’s exposure to light, but other hormones are also being studied.
Do we know what causes breast cancer ?
Many risk factors can increase your chance of developing breast cancer, but it is not yet known exactly how some of these risk factors cause cells to become cancerous. Hormones seem to play a role in many cases of breast cancer, but just how this happens is not fully understood. DNA is the chemical in each of our cells that makes up our genes—the instructions for how our cells function. We usually look like our parents because they are the source of our DNA. But DNA affects more than how we look. Some genes contain instructions for controlling when our cells grow, divide, and die. Genes that speed up cell division are called oncogenes. Others that slow down cell division, or cause cells to die at the right time, are called tumor suppressor genes. Certain changes (mutations) in DNA that “turn on†oncogenes or “turn off†tumor suppressor genes can cause normal breast cells to become cancerous.
Inherited gene mutations
Certain inherited DNA changes can increase the risk for developing cancer and are responsible for the cancers that run in some families. For example, the BRCA genes (BRCA1 and BRCA2) are tumor suppressor genes. Mutations in these genes can be inherited from parents. When they are mutated, they no longer suppress abnormal growth, and cancer is more likely to develop. Women have already begun to benefit from advances in understanding the genetic basis of breast cancer. Genetic testing can identify some women who have inherited mutations in the BRCA1 or BRCA2 tumor suppressor genes (or less commonly in other genes such as PTEN or TP53). These women can then take steps to reduce their risk of developing breast cancers and to monitor changes in their breasts carefully to find cancer at an earlier, more treatable stage. These are discussed in later sections of this document.
Acquired gene mutations
Most DNA mutations related to breast cancer occur in single breast cells during a woman’s life rather than having been inherited. These acquired mutations of oncogenes and/or tumor suppressor genes may result from other factors, like radiation or cancercausing chemicals. But so far, the causes of most acquired mutations that could lead to breast cancer are still unknown. Most breast cancers have several acquired gene mutations.
Tests to spot acquired gene changes may help doctors more accurately predict the outlook for some women with breast cancer. For example, tests can identify women whose breast cancer cells have too many copies of the HER2 oncogene. These cancers tend to be more aggressive. At the same time, drugs have been developed that specifically target these cancers.
Can breast cancer be prevented?
There is no sure way to prevent breast cancer. But there are things all women can do that might reduce their risk and help increase the odds that if cancer does occur, it is found at an early, more treatable stage.
Lowering your risk
You can lower your risk of breast cancer by changing those risk factors that can be changed (see the section, “What are the risk factors for breast cancer?”).
Body weight, physical activity, and diet have all been linked to breast cancer, so these might be areas where you can take action. Both increased body weight and weight gain as an adult are linked with a higher risk of breast cancer after menopause. Alcohol also increases risk of breast cancer. Even low levels of alcohol intake have been linked with an increase in risk. Many studies have shown that moderate to vigorous physical activity is linked with lower breast cancer risk.
A diet that is rich in vegetables, fruit, poultry, fish, and low-fat dairy products has also been linked with a lower risk of breast cancer in some studies. But it is not clear if specific vegetables, fruits, or other foods can lower risk. Most studies have not found that lowering fat intake has much of an effect on breast cancer risk.
At this time, the best advice about diet and activity to possibly reduce the risk of breast cancer is to:
• Get regular, intentional physical activity.
• Reduce your lifetime weight gain by limiting your calories and getting regular
physical activity.
• Avoid or limit your alcohol intake. For more information, see our document, American Cancer Society Guidelines on Nutrition and Physical Activity for Cancer Prevention.
Women who choose to breastfeed for at least several months may also get an added benefit of reducing their breast cancer risk. Not using hormone therapy after menopause can help you avoid raising your risk. It’s not clear at this time if environmental chemicals that have estrogen-like properties (like those found in some plastic bottles or certain cosmetics and personal care products) increase breast cancer risk. If there is an increased risk, it is likely to be very small. Still, women who are concerned may choose to avoid products that contain these substances when possible.
Finding breast cancer early
Other than lifestyle changes, the most important action a woman can take is to follow the American Cancer Society’s guidelines for early detection (outlined in the section, “Can breast cancer be found early?”). Early detection will not prevent breast cancer, but it can help find it when the likelihood of successful treatment is greatest.
For women who are or may be at increased risk
If you are a woman at increased risk for breast cancer (for example, because you have a strong family history of breast cancer, a known genetic mutation of a BRCA gene, or you have had DCIS, LCIS, or biopsies that have shown pre-cancerous changes), there may be some things you can do to reduce your chances of developing breast cancer. Before deciding which, if any, of these may be right for you, talk with your doctor to understand your risk and how much any of these approaches might lower this risk.
Genetic testing for BRCA gene mutations
Many women may have relatives with breast cancer, but in most cases this is not the result of BRCA gene mutations. Genetic testing for these mutations can be expensive and the results are often not clear cut. Testing can have a wide range of consequences that need to be considered. It should only be done when there is a reasonable suspicion that a mutation may be present.
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends that only women with a strong family history be evaluated for genetic testing for BRCA mutations. This group represents only about 2% of adult women in the United States. The USPSTF recommends that women who are not of Ashkenazi (Eastern European) Jewish heritage should be referred for genetic evaluation if they have any of the following:
• 2 first-degree relatives (mother, sisters, daughters) with breast cancer, one of whom
was diagnosed when they were younger than 50
• 3 or more first- or second-degree relatives (includes grandmothers, aunts) diagnosed
with breast cancer
• Both breast and ovarian cancer among first- and second-degree relatives
• A first-degree relative diagnosed with cancer in both breasts
• 2 or more first- or second-degree relatives diagnosed with ovarian cancer
• A male relative with breast cancer
Women of Ashkenazi (Eastern European) Jewish heritage should be referred for genetic evaluation if they have:
• A first-degree relative with breast or ovarian cancer
• 2 second-degree relatives on the same side of the family with breast or ovarian cancer
Other medical groups have different guidelines for referral for genetic risk evaluation that your doctor may follow. For example, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines advise referring women 60 and under who have triple negative breast cancer. If you are considering genetic testing, it is strongly recommended that you talk first to a genetic counselor, nurse, or doctor qualified to explain and interpret the results of these tests. It is very important to understand what genetic testing can and can’t tell you, and to carefully weigh the benefits and risks of testing before these tests are done. Testing is expensive and may not be covered by some health insurance plans. Most cancer centers employ a genetic counselor who will assess your risk of carrying a mutated BRCA gene, explain the risks and benefits of testing, and check with your insurance company to see if they will cover the test.
Breast cancer chemoprevention
Chemoprevention is the use of drugs to reduce the risk of cancer. Several drugs have been studied for lowering breast cancer risk.
Tamoxifen: Tamoxifen blocks some of the effects of estrogen on breast tissue. It has been used for many years to reduce the risk of recurrence in localized breast cancer and as a treatment for advanced breast cancer when the tumor is estrogen-receptor positive (see the section, “How is breast cancer treated?”). Tamoxifen can also lower the risk of getting breast cancer in women who are at increased risk for the disease. It seems to affect the risk of breast cancers that are estrogen receptor−positive (ER-postive), but not those that are estrogen receptor−negative (ERnegative). Most breast cancers that occur in women after menopause are ER-positive.
Results from the Breast Cancer Prevention Trial (BCPT) have shown that women at increased risk for breast cancer are less likely to develop the disease if they take tamoxifen. Women in the study took either tamoxifen or a placebo pill for 5 years. After 7 years of follow-up, women taking tamoxifen had 42% fewer breast cancers than women who took the placebo, although there was no difference in the risk of dying from breast cancer. Tamoxifen is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for reducing breast cancer risk in women at high risk. It can be used in women even if they haven’t gone through menopause.
Tamoxifen has side effects that include increased risks of endometrial (uterine) cancer (in women who have gone through menopause) and serious blood clots, so women should consider the possible benefits and risks of tamoxifen before deciding if it is right for them. And while tamoxifen seems to reduce breast cancer risk in women with BRCA2 gene mutations, the same may not be true for those with BRCA1 mutations.
Raloxifene: Like tamoxifen, raloxifene (Evista® ) also blocks the effect of estrogen on breast tissue. A study comparing the effectiveness of the 2 drugs in women after menopause, called the Study of Tamoxifen and Raloxifene (STAR) trial, found that raloxifene worked nearly as well as tamoxifen in reducing the risk of invasive breast cancer and non-invasive cancer (DCIS). Raloxifene also had lower risks of certain side effects such as uterine cancer and blood clots in the legs or lungs, compared to tamoxifen (although the risk of blood clots was still higher than normal). Like tamoxifen, it only lowers the risk of ER-postive breast cancer and not ER-negative tumors. Raloxifene is FDA approved to help reduce breast cancer risk in women past menopause who have osteoporosis (bone thinning) or are at high risk for breast cancer.
Aromatase inhibitors: Drugs such as anastrozole, letrozole, and exemestane are also being studied as breast cancer chemopreventive agents in post-menopausal women. These drugs, called aromatase inhibitors, are already being used to help prevent breast cancer recurrences. They work by blocking the production of small amounts of estrogen that post-menopausal women normally make. A recent study showed exemestane can lower the risk of invasive breast cancer by 65% in post-menopausal women who have an increased risk for breast cancer. Like tamoxifen and raloxifene, exemestane lowered the risk of breast cancers that are ER-positive, but not those that are ER-negative.
Exemestane and the other aromatase inhibitors can also have side effects, such as causing joint pain and stiffness. These drugs also can cause bone loss, leading to a higher risk ofosteoporosis. None of these drugs is currently FDA-approved for reducing the risk of developing breast cancer.
Other drugs: Studies are looking at other drugs as well. For example, some studies have found that women who take aspirin or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen seem to have a lower risk of breast cancer. Studies have also looked to see if drugs called bisphosphonates may lower the risk of breast cancer. Bisphosphonates are mainly used to treat osteoporosis, but they are also used to treat breast cancer that has spread to the bone. These, as well as several other drugs and dietary supplements, are being studied to see if they can lower breast cancer risk, but none is approved for reducing breast cancer risk at this time. Many of the drugs mentioned here are discussed further in the section, “How is breast cancer treated?” For more information on the possible benefits and risks of chemopreventive drugs see our document, Medicines to Reduce Breast Cancer Risk.
Preventive surgery for women with very high breast cancer risk
For the few women who have a very high risk for breast cancer, surgery to remove the breasts or ovaries may be an option.
Preventive (prophylactic) mastectomy: Removing both breasts before cancer is diagnosed can greatly reduce the risk of breast cancer (by up to 97%). Some women diagnosed with cancer in one breast choose to have the other, healthy breast removed as well to prevent a second breast cancer. Breast removal does not completely prevent breast cancer because even a very careful surgeon will leave behind at least a few breast cells.
The cells can go on to become cancerous. Some of the reasons for considering this type of surgery may include:
• Mutated BRCA genes found by genetic testing
• Strong family history (breast cancer in several close relatives)
• Lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) seen on biopsy
• Previous cancer in one breast (especially in someone with a strong family history)
While this type of surgery has been shown to be helpful in studies of large groups of women with certain conditions, there is no way to know ahead of time if this surgery will benefit any one woman. Some women with BRCA mutations will develop breast cancer early in life, and have a very high risk of getting a second breast cancer. Prophylactic mastectomy before the cancer occurs might add many years to their lives. But while most women with BRCA mutations develop breast cancer, some don’t. These women would not benefit from the surgery, but they would still have to deal with its after effects.
Second opinions are strongly recommended before any woman decides to have this surgery. The American Cancer Society Board of Directors has stated that “only very strong clinical and/or pathologic indications warrant doing this type of preventive operation.” Nonetheless, after careful consideration, this might be the right choice for some women.
Prophylactic oophorectomy (ovary removal): Women with a BRCA mutation may reduce their risk of breast cancer by 50% or more by having their ovaries surgically removed before menopause. This is likely because the surgery removes the main sources of estrogen in the body (the ovaries).
It is important that women with a BRCA mutation recognize they also have a high risk of developing ovarian cancer. Most doctors recommend that women with BRCA mutations have their ovaries surgically removed once they finish having children to lower this risk.
Can breast cancer be found early?
Screening refers to tests and exams used to find a disease, like cancer, in people who do not have any symptoms. The goal of screening exams, such as mammograms, is to find cancers before they start to cause symptoms. Breast cancers that are found because they can be felt tend to be larger and are more likely to have already spread beyond the breast. In contrast, breast cancers found during screening exams are more likely to be small and still confined to the breast. The size of a breast cancer and how far it has spread are important factors in predicting the prognosis (outlook) for a woman with this disease. Most doctors feel that early detection tests for breast cancer save many thousands of lives each year, and that many more lives could be saved if even more women and their health care providers took advantage of these tests. Following the American Cancer Society’s guidelines for the early detection of breast cancer improves the chances that breast cancer can be diagnosed at an early stage and treated successfully.
American Cancer Society recommendations for early breast cancer detection
Women age 40 and older should have a screening mammogram every year and should continue to do so for as long as they are in good health.
• Current evidence supporting mammograms is even stronger than in the past. In particular, recent evidence has confirmed that mammograms offer substantial benefit for women in their 40s. Women can feel confident about the benefits associated with regular mammograms for finding cance